Mobile health apps are becoming increasingly popular, and they provide opportunities for effective health management.
Existing chronic disease management (CDM) apps cannot meet users’ practical and urgent needs, and user adhesion is poor. Few studies, however, have investigated the factors that influence the continuance intention of CDM app users.
Objective: Starting from the affordances of CDM apps, this study aimed to analyze how such apps can influence continuance intention through the role of health empowerment.
Methods: Adopting a stimulus-organism-response framework, an antecedent model was established for continuance intention from the perspective of perceived affordances, uses and gratifications theory, and health empowerment. Perceived affordances were used as the “stimulus,” users’ gratifications and health empowerment were used as the “organism,” and continuance intention was used as the “response.” Data were collected online through a well-known questionnaire survey platform in China, and 323 valid questionnaires were obtained. The theoretical model was tested using structural equation modeling.
Results: Perceived connection affordances were found to have significant positive effects on social interactivity gratification (t717=6.201, P<.001) and informativeness gratification (t717=5.068, P<.001).
Perceived utilitarian affordances had significant positive effects
- on informativeness gratification (t717=7.029, P<.001),
- technology gratification (t717=8.404, P<.001),
- and function gratification (t717=9.812, P<.001).
Perceived hedonic affordances had
- significant positive effects on function gratification (t717=5.305, P<.001)
- and enjoyment gratification (t717=13.768, P<.001).
Five gratifications (t717=2.767, P=.005; t717=4.632, P<.001; t717=7.608, P<.001; t717=2.496, P=.012; t717=5.088, P<.001) had significant positive effects on health empowerment.
Social interactivity gratification, informativeness gratification, and function gratification had significant positive effects on continuance intention.
Technology gratification and enjoyment gratification did not have a significant effect on continuance intention.
Health empowerment had a significant positive effect on continuance intention. Health empowerment and gratifications play mediating roles in the influence of affordances on continuance intention.
Conclusions: Health empowerment and gratifications of users’ needs are effective ways to promote continuance intention. The gratifications of users’ needs can realize health empowerment and then inspire continuance intention. Affordances are key antecedents that affect gratifications of users’ needs, health empowerment, and continuance intention.
The results indicated that users’ perceptions of an app’s affordances can promote the gratification of needs, and the gratification of key needs (ie, social interactivity, informativeness, technology, and function gratification) can stimulate users’ continuance intention. At the same time, the gratification of users’ needs can promote users’ cognitions of health empowerment, thus stimulating continuance intention. Health empowerment was found to play a mediating role in the influence of gratification on continuance intention. From a practical perspective, app service providers should design apps from the perspective of social interaction (eg, providing social networks), utilitarian functions (eg, health self-management), and hedonic functions (eg, enhancing the user’s interest). By meeting users’ various needs, app developers can improve the user’s ability to control his or her own health, thus achieving the purpose of extending the life of the app.
more at https://mhealth.jmir.org/2021/5/e21831/



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...






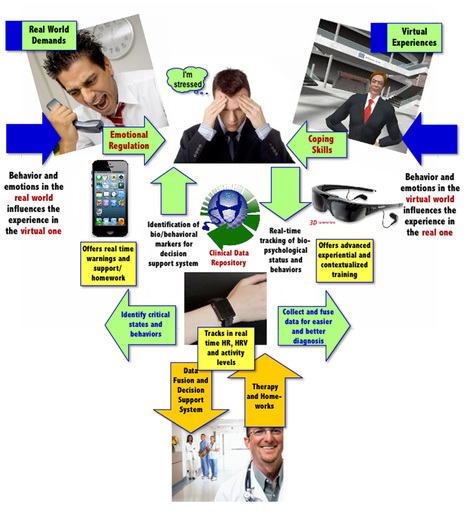






Common approaches to assess the symptoms of patients in long term treatments, currently in practice, include
These are time-consuming and often complex.
With the popularity of smartphones and mobile internet, remote network technology is changing traditional medical behavior