The past several decades have seen an alarming spike in communicable disease outbreaks worldwide. Given a confluence of host, virologic, environmental, and human factors, experts agree that the next pandemic could already be on the horizon.
In a globalized world, changes in how people use land and interact with their ecosystems—such as rapid deforestation and agricultural expansion—have resulted in humans and animals coming into more frequent and intense contact with one another, increasing opportunities for what is known as "zoonotic disease spillover."
In the past few years alone, numerous disease outbreaks have had suspected or confirmed zoonotic origin, including mpox (formerly known as monkeypox), Ebola virus disease, dengue fever, and COVID-19.
Experts also recognize the need to prepare for another possible Disease X, a term used to describe a currently unknown pathogen with pandemic potential.
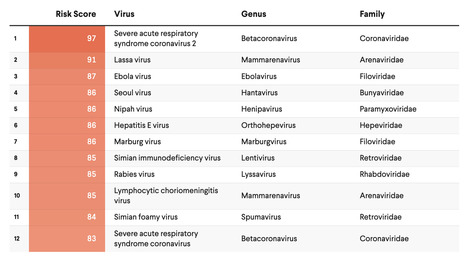
To direct resources toward the most high-consequence pathogens, it is paramount that leaders have an accurate concept of pandemic risk—for individual viruses as well as viral families. Several institutions are developing disease rankings at national and global levels, including the Priority Zoonotic Diseases Lists facilitated by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Research and Development (R&D) Blueprint created by the World Health Organization.
The original SpillOver risk ranking framework (SpillOver 1.0), an open-source webtool launched by researchers at the University of California, Davis One Health Institute, estimated the relative spillover potential of wildlife-origin viruses to humans based on a series of host, viral, and environmental risk factors determined via expert opinion and scientific evidence.
Its next iteration, SpillOvers 2.0, has rebranded to better describe the diversity and frequency of virus spillovers to people. The new platform uses a One Health approach, which recognizes the interdependence of human, animal, and environmental health. It will expand to include domestic animal and vector-borne viruses and assess pandemic risk rather than just spillover risk for wildlife viruses.



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...